Solid State Drives are great. If you switch from a platter-based drive to a SSD you will think you are in speed-heaven for the first time. Windows boots faster, programs start faster and everything seems to be improved speed-wise.
With the first generation of Solid State Drives, things deteriorated quickly due to limited write cycles and controllers that were far from optimal.
New generation drives, like the Samsung 850 Evo, benefit from better firmware and controllers, which makes them more durable and faster.
Drives did benefit from new operating system versions as well. Windows 7 introduced TRIM and Windows 8 came along with its own set of optimizations specifically for Solid State Drives.
Common Wisdom is that Solid State Drives should not be defragmented. This is based on the fact that SSDs support limited writes and that defrag operations cause many writes on the device.
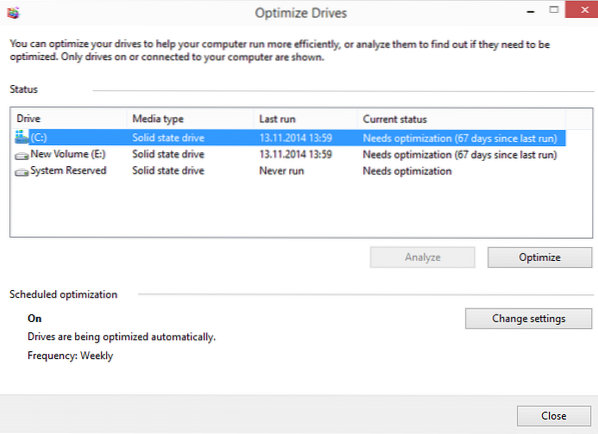
If you have installed Windows 8 on a system with a Solid State Drive or bought a PC with one running the operating system, you may have noticed that defrag runs on the Solid State Drive at times.
You may also have read about it on various blogs on the Internet.
If you check your system with a program like Check Boot Speed you get a detailed report that includes defragmentation information so that you know if your SSD gets defragmented or not.
Is defragmentation good or bad on SSDs?
The question that needs to be answered is whether that is a good thing that is done on purpose or a bug.
Microsoft confirmed to Scott Hanselman (who is a member of Microsoft's Web Platform Team) recently that Windows defragments Solid State Drives sometimes under Windows 8 (and probably newer versions as well) and that it does so on purpose.
SSDs are defragmented every 28 days on Windows 8 and newer if Volume Snapshots are enabled (the feature is used by System Restore and thus enabled by default) on the system. Defragmentation occurs if a drive is highly fragmented which slows down the read and write process on drives because of additional metadata that needs to be processed.
In addition, it is possible that drives hit maximum file fragmentation (when metadata cannot represent more file fragments) which will result in errors when trying to write or extend the file.
The underlying issue seems to be a limitation of the file system in regards to fragments and that Microsoft's workaround for it is to use defrag to reduce the number of fragments.
This makes defrag on SSDs a necessity under Windows even though that means additional writes on the system.
 Phenquestions
Phenquestions