In the recent past, there has been a bit of debate on which Python version should one learn. Python 2 or Python 3. It's now 2020 and pretty evident that Python 3 is the way to go. However, Python 2 is still in the market, and some people, including me, still use it in development. It brings forth the necessity of how we set up and switch between the two versions on your Linux system.
Ubuntu 18.04 LTS release came with several changes, and one is that Python 2 was no longer the default Python version in the system. Welcome, Ubuntu 20.04 LTS release; canonical dropped Python 2 entirely and no longer included it among the installation packages.
See the image below. When we try to execute the Python 2 command, which is by default “python,” we get “command not found” error.
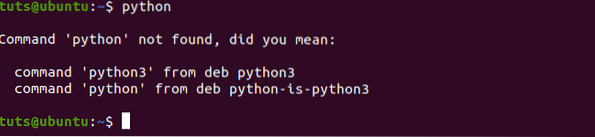
In this post, we will show you how to:
- Install Python 2 in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- Switch between Python 3 and Python 2 versions
Installing Python 2 in Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
Step 1) Launch the Terminal and type any of the commands below. You will be required to enter your root password.
$ sudo apt install python2 OR $ sudo apt install python-minimal
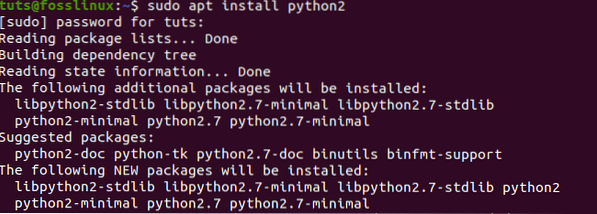
Step 2) Once the installation complete, you can check the Python 2 version using the “-version” command.
python2 --version python3 --version
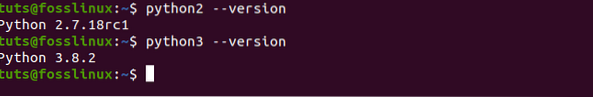
From the image above, we can see we are running Python 2.7 and Python 3.8. Now, let's jump on to one of the important parts of this tutorial of how to configure Python and switch between the two versions - Python 2 and Python 3.
How to switch between Python 2 and 3 versions on Ubuntu 20.04
Method 1: My recommended way by configuring
Step 1) Check all the available Python versions in your system. To do so, we will need to check the /bin directory. That is because we can have variations in Python 3. Say Python 3.7 and Python 3.8. In such situations, the -version command won't be useful as it only lists the currently configured version.
Execute the commands below on the Terminal.
ls /usr/bin/python*
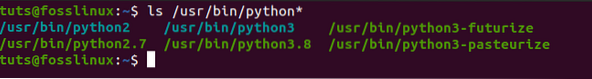
Step 2) Once we have listed all the versions present on the system, we need to check whether there are any Python-alternatives configured.
Execute the command below on the Terminal.
sudo update-alternatives --list python
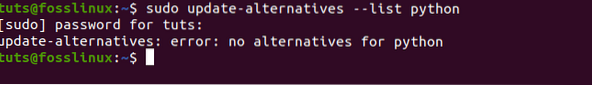
From the image above, we see that there are no Python alternatives configured.
Step 3) Now, we will configure two Python alternatives. From the image in Step 2 above, we saw that I have Python 2.7 and Python 3.8 present on my system.
Execute the commands below on the Terminal.
$ sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python2 1 $ sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3 2
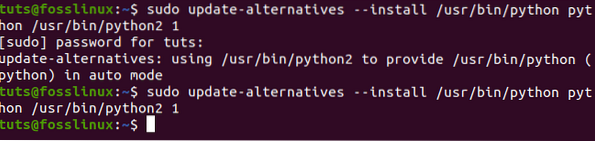
Step 4) We need to confirm the Python alternatives set and whether they are in use.
Execute the command below again.
$ sudo update-alternatives --config python
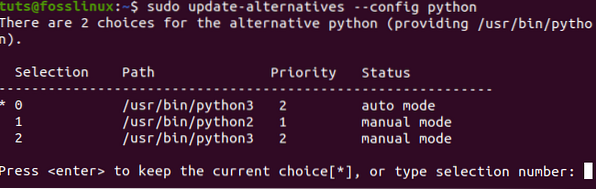
On the prompt that appears on the Terminal, enter 1 or 2 to make your selection. In this post, we want to use Python 2; therefore, we will enter option 1.
Step 5) Now, let's check the Python version currently running on our system. Execute the command below.
python --version

To switch to another Python version, all you need to do is execute the command on Step 4 and select the other option. In this case, we would choose option 2 to use Python 3.
Method 2: Old-school way without configuration
This other method, we would refer to it as the manual way since we won't perform any configurations. Follow the procedure below.
Step 1) Install Python 2 with the command below.
sudo apt install python2
Step 2) Check the Python versions present in your system by running the command below.
ls /usr/bin/python*

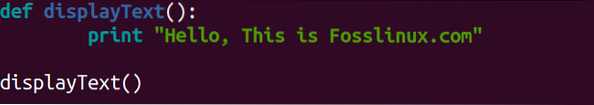
Step 3) In this post, we currently have Python 2 and Python 3 available. Now write your Python 2 or Python 3 code.
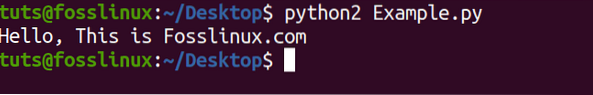
For example, below is a Python 2 code to print the sentence “Hello, This Fosslinux.com.“
Step 4) To execute your code using Python 2, you will need to specify the version manually. For example, the python file is called Example.py. Execute the command below.
python2 Example.py
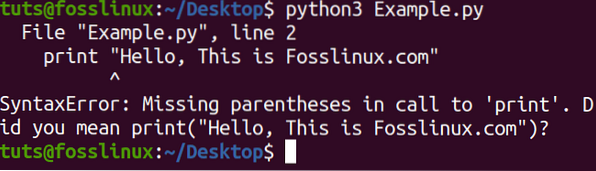
If we used Python 3 to execute the code below, we would get an error, as shown below.
If we were writing code using Python 3, we would specify Python 3 when running the program.
Conclusion
Despite Python 2 being dropped in the recent Linux releases, some people still find it advantageous and use it in their development. There are vast applications built using Python 2, and the transition to Python 3 has not been put into effect fully.
These and many other reasons make Python 2 still relevant in the development community. With the methods described above, you will be able to switch from one Python version to another easily when coding.
 Phenquestions
Phenquestions



